The OSI Model and Cybersecurity Protection Guide
What is the OSI Model?
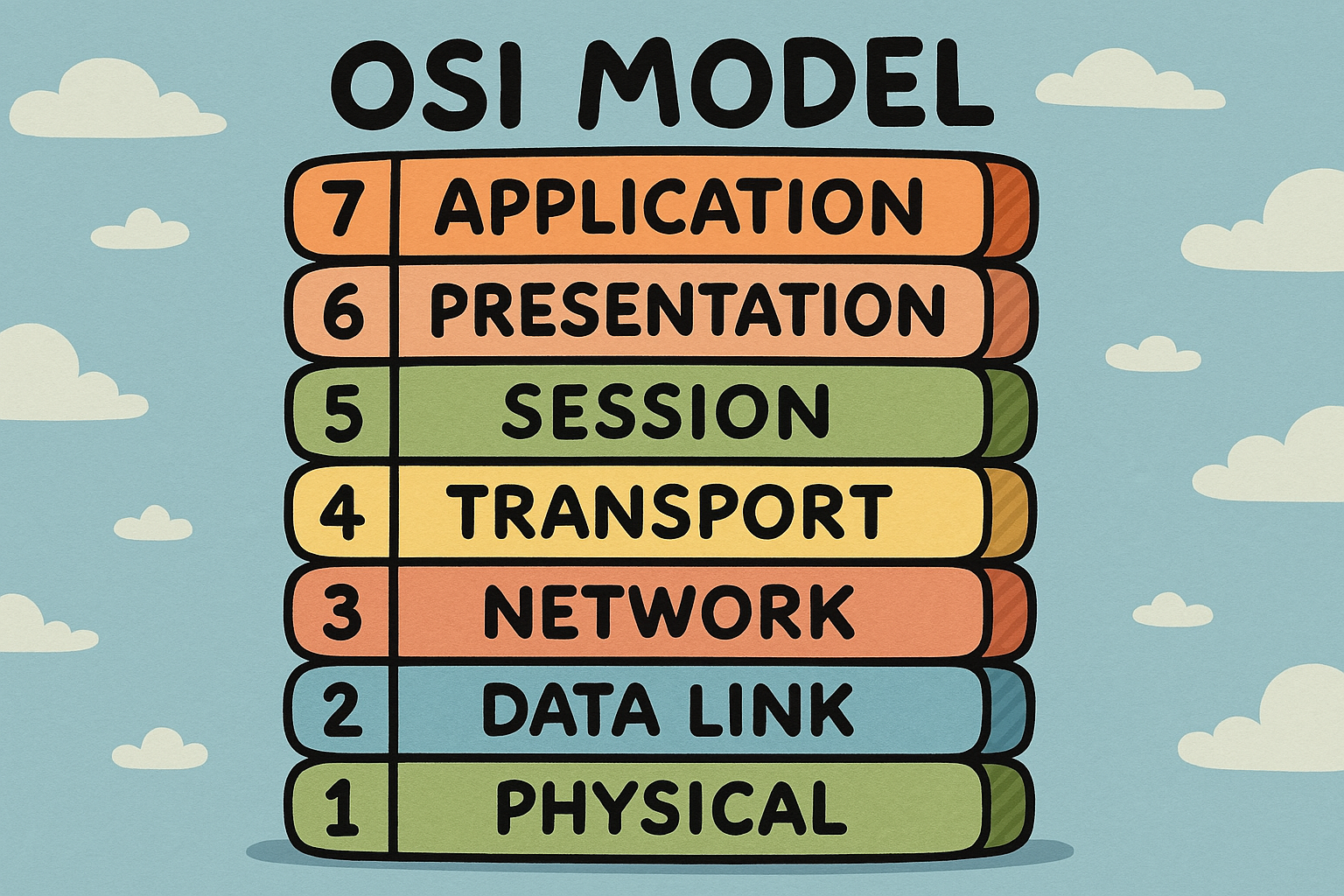
The OSI (Open Systems Interconnection) model is a framework that breaks down network communication into seven distinct layers. Think of it like a postal system - your message goes through multiple stages from writing it to delivery, with each stage having specific responsibilities.
The Seven Layers Explained
Layer 7 - Application Layer
This is what you actually interact with - web browsers, email clients, social media apps. It's where human-readable data lives.
Layer 6 - Presentation Layer
Handles data formatting, encryption, and compression. It translates data between different formats so applications can understand each other.
Layer 5 - Session Layer
Manages connections between applications. It establishes, maintains, and terminates communication sessions between devices.
Layer 4 - Transport Layer
Ensures reliable data delivery using protocols like TCP and UDP. It handles error correction and data flow control.
Layer 3 - Network Layer
Routes data between different networks using IP addresses. This is where routers operate to find the best path for your data.
Layer 2 - Data Link Layer
Manages communication between devices on the same network segment. It handles MAC addresses and error detection.
Layer 1 - Physical Layer
The actual hardware - cables, wireless signals, network cards. It transmits raw electrical signals or radio waves.
Cybersecurity Threats by Layer
Application Layer Threats:
- Malware and viruses
- Phishing attacks
- SQL injection
- Cross-site scripting (XSS)
- Social engineering
Presentation Layer Threats:
- Encryption attacks
- Data manipulation
- Format string attacks
Session Layer Threats:
- Session hijacking
- Man-in-the-middle attacks
- Session replay attacks
Transport Layer Threats:
- Port scanning
- TCP/UDP flooding
- Protocol exploitation
Network Layer Threats:
- IP spoofing
- Routing attacks
- DDoS attacks
- Network reconnaissance
Data Link Layer Threats:
- ARP poisoning
- MAC address spoofing
- Switch attacks
Physical Layer Threats:
- Cable tapping
- Physical device theft
- Electromagnetic interference
- Hardware tampering
Protection Methods for Each Layer
For Businesses
Application Layer Protection:
- Deploy comprehensive antivirus and anti-malware solutions
- Implement web application firewalls (WAF)
- Conduct regular security awareness training
- Use secure coding practices
- Perform regular vulnerability assessments
- Deploy endpoint detection and response (EDR) solutions
Presentation Layer Protection:
- Use strong encryption protocols (AES-256, TLS 1.3)
- Implement proper certificate management
- Deploy data loss prevention (DLP) solutions
- Use secure file transfer protocols
Session Layer Protection:
- Implement session timeout policies
- Use secure session management
- Deploy network access control (NAC)
- Monitor session activities
Transport Layer Protection:
- Configure firewalls to block unnecessary ports
- Implement intrusion detection systems (IDS)
- Use load balancers for traffic distribution
- Deploy DDoS protection services
Network Layer Protection:
- Segment networks using VLANs
- Implement next-generation firewalls (NGFW)
- Use VPN for remote access
- Deploy network monitoring tools
- Implement zero-trust architecture
Data Link Layer Protection:
- Use managed switches with security features
- Implement port security
- Deploy network admission control
- Monitor for abnormal MAC address activities
Physical Layer Protection:
- Secure server rooms and network closets
- Use surveillance systems
- Implement badge access controls
- Regular security audits of physical infrastructure
- Use tamper-evident seals on equipment
For Social Media Users
Application Layer Protection:
- Keep apps and browsers updated
- Use reputable antivirus software
- Be cautious with links and downloads
- Enable two-factor authentication
- Review privacy settings regularly
- Avoid public Wi-Fi for sensitive activities
Presentation Layer Protection:
- Use HTTPS websites (look for the lock icon)
- Keep personal information private
- Be careful what you share in posts and messages
Session Layer Protection:
- Log out of accounts when finished
- Don't stay logged in on public computers
- Monitor active sessions in account settings
Transport Layer Protection:
- Use secure networks when possible
- Avoid suspicious network connections
- Consider using a personal VPN
Network Layer Protection:
- Use home network security features
- Change default router passwords
- Keep router firmware updated
- Use a VPN on public networks
Data Link Layer Protection:
- Secure your home Wi-Fi with WPA3
- Don't connect to unknown networks
- Use network names that don't reveal personal information
Physical Layer Protection:
- Keep devices physically secure
- Use screen locks and device encryption
- Don't leave devices unattended in public
- Be aware of shoulder surfing
Best Practices Summary
For Businesses:
- Implement defense in depth across all layers
- Regular security assessments and penetration testing
- Employee training and awareness programs
- Incident response planning
- Regular backup and disaster recovery testing
- Compliance with industry standards (ISO 27001, NIST)
For Social Media Users:
- Practice good digital hygiene
- Stay informed about new threats
- Use strong, unique passwords with a password manager
- Be skeptical of unsolicited messages or friend requests
- Regularly review and update privacy settings
- Think before you post or share
The key to effective cybersecurity is understanding that protection must happen at every layer. No single security measure is sufficient - you need multiple overlapping defenses to create a robust security posture. By understanding how the OSI model works and where vulnerabilities can occur, both businesses and individuals can make more informed decisions about their cybersecurity strategies.