Automate Your File Management: Bulk Rename Files with Python
Have you ever downloaded a batch of files only to find they all have messy, auto-generated prefixes that make them hard to organize? If you're like me and prefer clean, readable file names, manually renaming dozens of files one by one is the last thing you want to spend your time on.
In this tutorial, I'll show you how I solved this exact problem using a simple Python script that automatically removes unwanted prefixes from file names in bulk.
The Problem: Messy File Names
Recently, I subscribed to Scribd.com for a month to download e-books for my collection. While I love the convenience of e-books and use readers like Amazon Kindle and Readera, there was one annoying issue: all downloaded files came with gibberish prefixes that made them look like this:
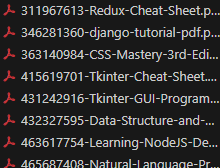
xK9p2mQ-book-title.pdf
7Hf3nWt-another-great-book.epub
bR8sLv4-programming-guide.pdf
Instead of spending precious reading time manually renaming each file, I decided to automate the process with Python.
The Solution: Python Automation
The approach is straightforward: identify a consistent pattern in the unwanted prefixes and write a script to remove everything before that pattern.
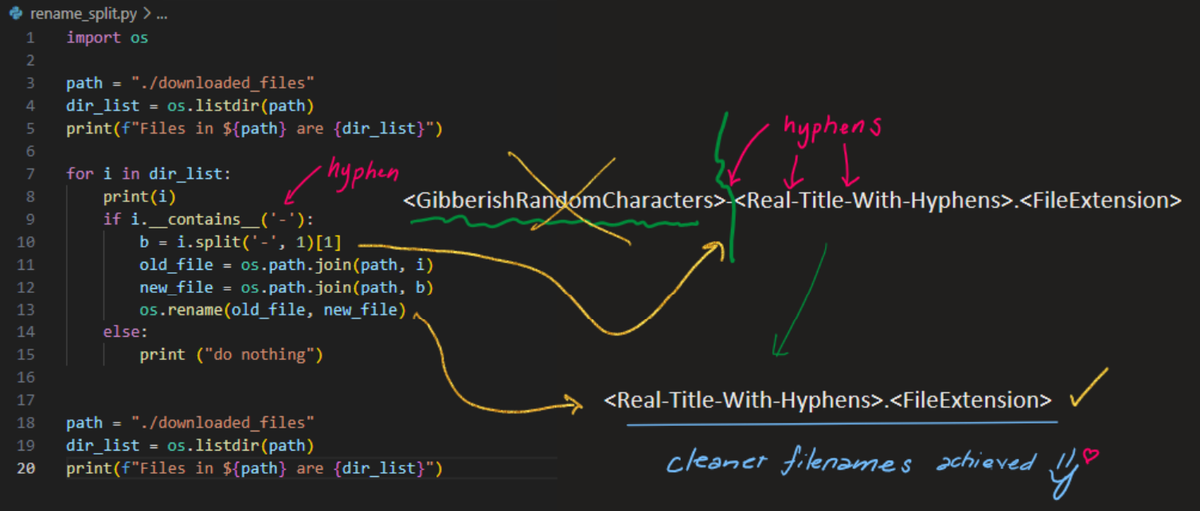
In my case, all files had the same structure: [gibberish-code]-[actual-filename]. The solution was to find the first hyphen and keep only the part after it.
The Python Script
Here's the complete script that solved my problem:
import os
def rename_files_in_directory(directory_path):
"""
Rename files by removing everything before the first hyphen
"""
# Get list of all files in the directory
files = os.listdir(directory_path)
renamed_count = 0
for filename in files:
# Skip directories
if os.path.isdir(os.path.join(directory_path, filename)):
continue
# Check if filename contains a hyphen
if '-' in filename:
# Find the first hyphen and get everything after it
new_name = filename.split('-', 1)[1]
# Get full file paths
old_path = os.path.join(directory_path, filename)
new_path = os.path.join(directory_path, new_name)
# Rename the file
try:
os.rename(old_path, new_path)
print(f"Renamed: {filename} → {new_name}")
renamed_count += 1
except OSError as e:
print(f"Error renaming {filename}: {e}")
print(f"\nTotal files renamed: {renamed_count}")
# Usage
if __name__ == "__main__":
# Replace with your directory path
directory_path = "/path/to/your/files"
rename_files_in_directory(directory_path)
How It Works
- Directory Scanning: The script lists all files in the specified directory
- Pattern Matching: For each file, it checks if there's a hyphen in the filename
- String Splitting: Uses
split('-', 1)to split the filename at the first hyphen only - File Renaming: Renames the file using
os.rename()with proper error handling - Progress Tracking: Prints the rename operations and counts total files processed
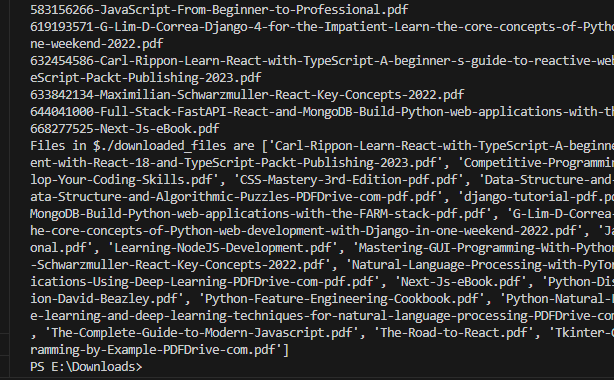
Before and After
Before running the script:
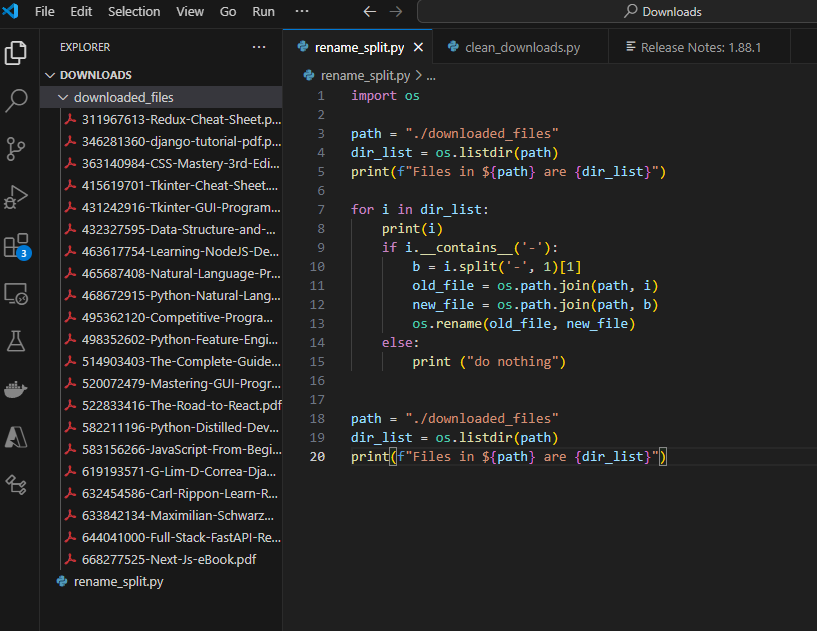
xK9p2mQ-The-Art-of-Programming.pdf
7Hf3nWt-Data-Science-Handbook.epub
bR8sLv4-Machine-Learning-Guide.pdf
After running the script:
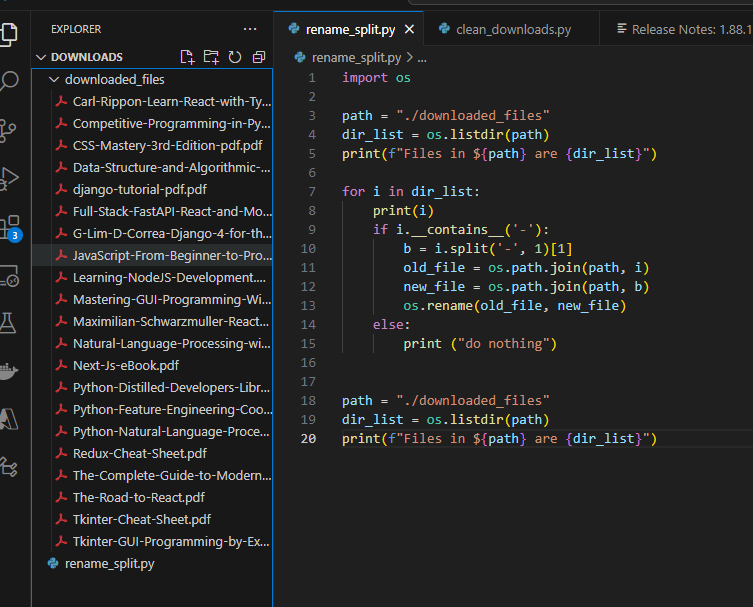
The-Art-of-Programming.pdf
Data-Science-Handbook.epub
Machine-Learning-Guide.pdf
Customizing the Script
The beauty of this approach is its flexibility. You can easily modify it for different patterns:
Remove Everything Before the Last Underscore
new_name = filename.rsplit('_', 1)[1]
Remove Specific Prefix Length
new_name = filename[8:] # Remove first 8 characters
Remove Multiple Patterns
import re
new_name = re.sub(r'^[A-Za-z0-9]+-', '', filename)
Safety Tips
Before running any bulk rename script:
- Backup Your Files: Always work on a copy of your files first
- Test on a Small Batch: Run the script on a few files to verify it works as expected
- Check for Duplicates: Ensure the new names won't create conflicts
- Use Verbose Output: The print statements help you see what's happening
Advanced Features You Could Add
- Dry Run Mode: Preview changes without actually renaming files
- Recursive Directory Processing: Handle subdirectories automatically
- File Type Filtering: Only process specific file extensions
- Undo Functionality: Keep a log to reverse changes if needed
Conclusion
Automating repetitive tasks like file renaming not only saves time but also reduces the chance of human error. With just a few lines of Python code, you can transform a tedious manual process into a quick, reliable operation.
Whether you're organizing downloaded e-books, cleaning up photo collections, or managing any other bulk files, Python's file handling capabilities give you complete control over your file management workflow.
The next time you face a similar challenge, remember: if you're doing something repetitive more than a few times, there's probably a way to automate it. Your future self will thank you for the time saved and the headache avoided.